Advanced Ultrasound & CT Scan
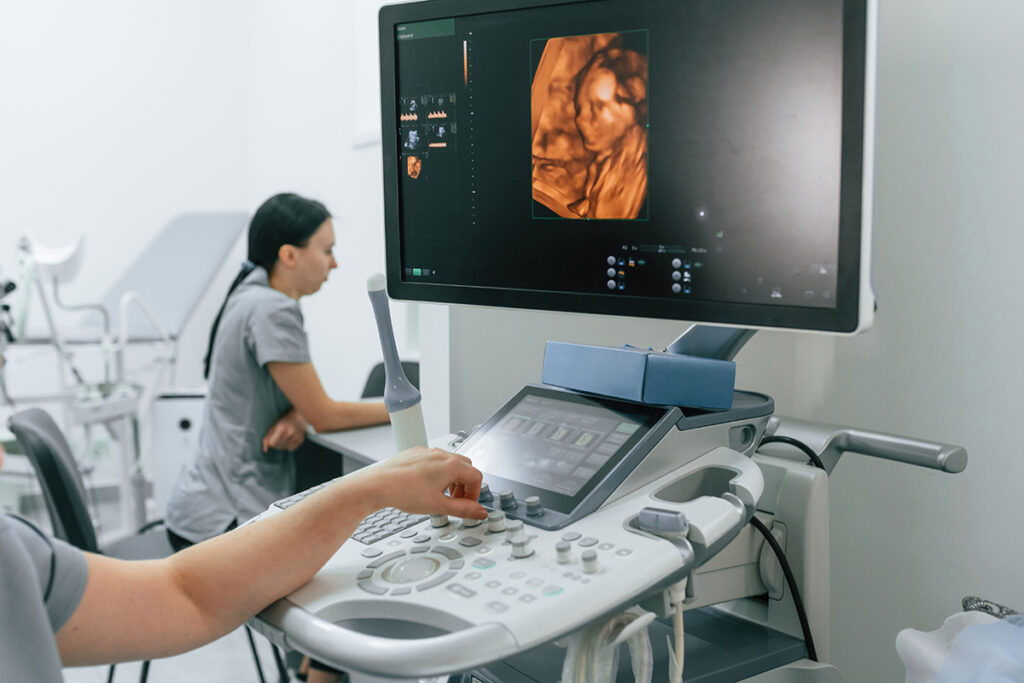
Advanced Ultrasound
Advanced 3D ultrasound is an effective diagnostic tool for evaluating urological disorders. Your doctor may recommend an ultrasound examination of the kidney, ureter, and bladder region to screen for various urinary tract issues such as infections, stones, and tumors. While this technique provides detailed images, ureteric stones can sometimes be difficult to visualize clearly due to interference from intestinal gas. To enhance the examination, you will be asked to drink water beforehand to ensure your bladder is full, improving image quality. Unlike some other ultrasounds, you do not need to fast or have an empty stomach before a kidney, ureter, and bladder (KUB) ultrasound, making it a convenient and non-invasive test.
Advanced CT Scan
It is part of advanced evaluation based on initial findings of Ultrasound. The doctor may ask for Plain or a Contrast CT scan depending upon indication. It is a very good modality for the detection of stones in the urinary tract. apart from the measurement of exact location and size it also informs about the hardness of stone which is important for deciding treatment modality. It also gives anatomical details to inform about the condition of kidney Ureter & bladder.
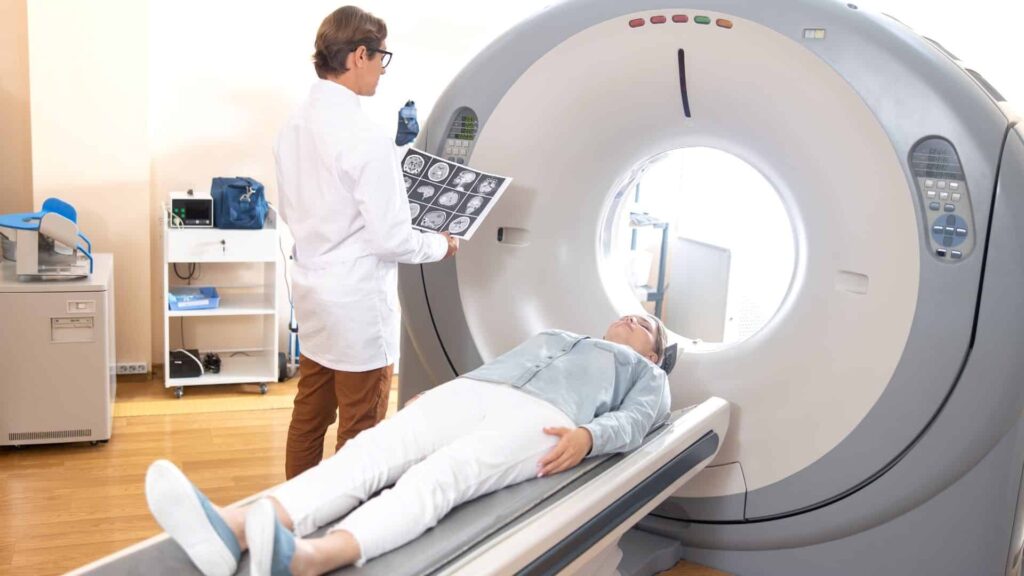

Advanced CT Scan
People scheduled for a cystoscopy should ask their doctor about any special instructions.

