Treatment Options for Kidney Stones: From Medication to Surgery
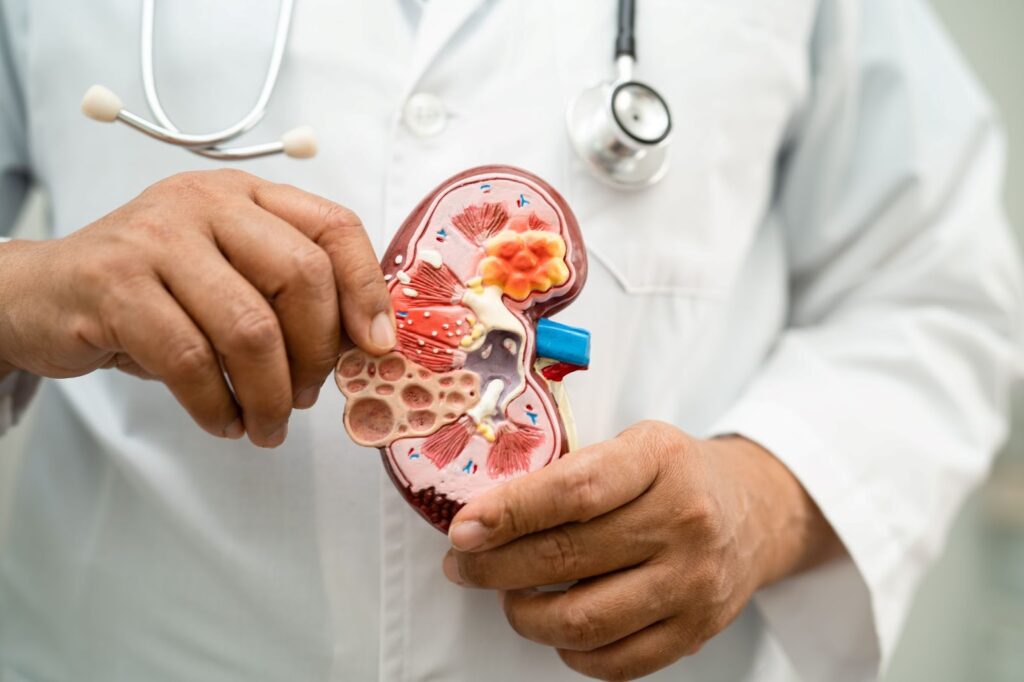
Understanding Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form inside the kidneys, often causing severe pain and urinary complications. They develop when certain substances in urine, like calcium, oxalate, and phosphorus, become concentrated enough to crystallize and harden. Various factors contribute to kidney stone formation including dehydration, diet high in salt and animal protein, obesity, certain medical conditions such as diabetes and gout, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms and Warning Signs Symptoms of kidney stones vary depending on the size and location of the stone. Small stones may pass without causing noticeable symptoms. However, larger stones can block urine flow, causing sharp, cramping pain typically felt in the side or lower back that radiates towards the groin. Other symptoms include blood in urine, nausea, vomiting, frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, fever, and chills in case of infection. Diagnosis Diagnosing kidney stones involves a physical examination, review of medical history, and imaging tests such as CT scans, ultrasounds, or X-rays to locate and measure the stones. Blood and urine tests help identify underlying causes and assess kidney function that guides treatment decisions. Treatment Options Treatment depends on the stone’s size, type, and symptoms. Small stones often pass naturally with adequate hydration and pain management using medications like NSAIDs or acetaminophen. Doctors may prescribe alpha-blockers to relax urinary tract muscles and facilitate stone passage. For larger stones, or if stones cause obstruction, infection or persistent pain, more advanced interventions are necessary: Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): Uses sound waves to break stones into smaller fragments for easier passage. Ureteroscopy: A fine scope removes or breaks stones in the ureter or kidney. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Surgical removal of large or complex stones through a small back incision. Prevention Preventive strategies focus on lifestyle and dietary changes: Drink plenty of water daily to dilute urine and reduce crystallization risk. Limit salt, animal protein, and foods high in oxalate like spinach and nuts. Maintain a healthy weight and manage underlying conditions (such as diabetes). Regular medical check-ups to monitor and prevent recurrence. Kidney stones can be intensely painful but are highly treatable with modern medical approaches. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment by specialists like Dr. Neeraj Agrawal can provide relief and minimize complications, enhancing patient well-being and kidney health. Empowering patients with knowledge and preventive care is essential to reduce the incidence and impact of kidney stones, ensuring healthier urinary tract function and improved quality of life.