Pain Abdomen/Flank
What is Flank Pain & Where is Located?
Flank pain is pain in one or both sides of your abdomen. Certain injuries, diseases and infections can cause pain in your flanks. Flank pain can range from mild to severe — it may be a dull ache or a sharp pain. It may come and go. It’s usually worse on one side. But it can occur on both flanks.
Where are the flanks located?
Your flanks are the areas on the sides and back of your abdomen, between your lower ribs and your hips.
How common is flank pain?
Flank pain is very common. Most people get flank pain at some point in their lives. It’s usually not a cause for concern. But it’s a good idea to reach out to a healthcare provider if you have severe flank pain that lasts more than a few days.
Possible Causes Of Flank Pain
Flank pain has several possible causes, ranging from minor muscle strains to serious medical conditions. Common causes include muscle problems such as strains, overuse, and spasms, especially after physical activity or prolonged poor posture. Kidney-related issues are another frequent cause, including kidney stones, infections (such as pyelonephritis), kidney abscesses, or kidney diseases like polycystic kidney disease. Flank pain can also be a result of urinary tract infections, gallbladder disease, liver disease, spinal problems like herniated discs or arthritis, and even infections such as shingles. Each condition requires specific attention, particularly if accompanied by symptoms like fever, urinary changes, or rash
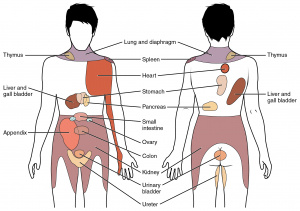
What organs can cause flank pain?
Conditions that affect the following organs can cause flank pain:
- Kidneys
- Liver
- Urinary bladder
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on what’s causing your flank pain. A healthcare provider may recommend:
Rest and use of over-the-counter pain relievers (NSAIDs or analgesics) may help reduce muscle strain-related flank pain.
Prescription pain medications can be used for more severe discomfort, always under medical guidance.
Physical therapy, stretching, and exercise help strengthen spinal and back muscles, lowering the risk of recurrent pain.
Antibiotics are necessary if a bacterial infection such as a UTI or kidney infection is the cause.
Extra fluid intake can assist with passing kidney stones, and procedures like lithotripsy or ureteroscopy may be required for large or stubborn stones.
Surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy may be needed for cancer-related conditions affecting the kidneys or urinary system.
Prevention Strategies
You may not be able to prevent every cause of flank pain. But you can reduce your risk of kidney problems, injuries and diseases by:
Stay well-hydrated to maintain kidney health and reduce the risk of stones.
Eat a balanced diet, limit sodium, and avoid foods high in animal protein to protect kidney function.
Maintain a healthy weight and regular physical activity to prevent injuries and reduce strain on the spine.
Practice good urinary hygiene to prevent UTIs: urinate after sexual activity, wipe from front to back, and avoid holding urine for long periods.
Schedule regular medical check-ups, keep up to date with vaccinations, and discuss preventive care with a healthcare professional.

